Practical Arduino C
Chapter 16: Extras
NTP Server
The code on page 263 of the book (and below) includes a hard coded IP address for one of the pool.ntp.org time servers. This address has changed and is likely to change again (currently 129,250,35,250). It is a good idea to check the current value by opening a new command window and using the "ping" command to ping the server. The response shoud confirm the current value. For example:
C:\Users\mike>ping 0.uk.pool.ntp.org
Pinging 0.uk.pool.ntp.org [129.250.35.250] with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 129.250.35.250: bytes=32 time=14ms TTL=60
Reply from 129.250.35.250: bytes=32 time=12ms TTL=60
Reply from 129.250.35.250: bytes=32 time=12ms TTL=60
Reply from 129.250.35.250: bytes=32 time=14ms TTL=60
Ping statistics for 129.250.35.250:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 12ms, Maximum = 14ms, Average = 13ms
The best results will always be obtained by doing an internet search for the address of a time server local to you.
IP Address Solution
When I later returned to the programs explored in this chapter I went looking for a way to obtain a current IP address for an NTP time server URL. While the IP addresses change the URL is pretty constant. I found an answer and blogged a nice method for this.
Page 258
Page 259
const int PWMA = 4;
const int AIN2 = 3;
const int AIN1 = 2;
const int STBY = 1;
const int INTPIN = 0;
int motorASpeed = 255;
//volatile bool stopA = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000);
pinMode(PWMA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(AIN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(AIN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(STBY, OUTPUT);
pinMode(INTPIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
//attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(INTPIN), setStopA, LOW);
test1();
}
void motorAForward() {
Serial.println("Forward");
analogWrite(PWMA, motorASpeed);
digitalWrite(AIN1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(AIN2, LOW);
digitalWrite(STBY, HIGH);
}
void motorABrake() {
Serial.println("Brake");
digitalWrite(AIN1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(AIN2, HIGH);
analogWrite(PWMA, 0);
}
void motorAStop() {
Serial.println("Stop");
digitalWrite(AIN1, LOW);
digitalWrite(AIN2, LOW);
analogWrite(PWMA, 0);
digitalWrite(STBY, LOW); // would also stop motor B
}
void motorABack() {
Serial.println("Backward");
analogWrite(PWMA, motorASpeed);
digitalWrite(AIN1, LOW);
digitalWrite(AIN2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(STBY, HIGH);
}
Page 260
void test1() {
motorAForward();
delay(2000);
motorABrake();
delay(500);
motorAStop();
delay(1000);
motorABack();
delay(2000);
motorABrake();
delay(500);
motorAStop();
}
void setStopA() {
stopA = true;
}
void loop() {
if(stopA) {
motorAStop();
Serial.println("Limiter Stop");
stopA = false;
}
}
Page 261
#include <WiFiNINA.h>
template<class T> inline Print &operator<<(Print &obj, T arg) {
obj.print(arg); return obj;}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) {}
Serial.println("Scanning available WiFi access...");
listWiFi();
}
void listWiFi() {
int wifiCount = WiFi.scanNetworks();
for(int i = 0; i < wifiCount; i++) {
Serial << i << ' ' << "SSID: " << WiFi.SSID(i) << '\n';
}
if(wifiCount < 1) {
Serial.println("No WiFi services found");
}
}
void loop() {
}
Page 262
#include <WiFiNINA.h>
#include "Secret.h"
const char* mySSID = SECRET_SSID;
const char* myPass = SECRET_PASSWORD;
template<class T> inline Print &operator<<(Print &obj, T arg) {
obj.print(arg); return obj;}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) {}
Serial.println("Connecting to WiFi...");
connectToWiFi();
}
void connectToWiFi() { while (WiFi.begin(mySSID, myPass) != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
}
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
Serial << "Local IP: " << WiFi.localIP() << '\n';
}
Serial << "Signal strength: " << WiFi.RSSI() << '\n';
byte macAdd[6];
WiFi.macAddress(macAdd);
Serial.print("MAC Address: ");
showMACAddress(macAdd);
void showMACAddress(byte add[]) {
for(int i = 5; i >= 0; i--) {
if(add[i] < 16) {Serial.print('0');} // padd hex
Serial.print(add[i], HEX);
if(i > 0) {
Serial.print(':');
}
}
Serial.println();
}
Page 263
Please see the comments on checking for a current time server IP address and a blogged solution at the top of this web site page.
unsigned int localPort = 2390; // local port to listen for packets
IPAddress timeServer(143,210,16,201); // 0.uk.pool.ntp.org note commas
const int NTP_PACKET_SIZE = 48; // NTP time stamp in the first 48 bytes
byte packetBuffer[NTP_PACKET_SIZE]; //buffer to hold packets
const int GMT_ADJUST = 1 * 60 * 60; //time zone adjustment (BST)
unsigned long epoch;
void getCurrentTime() {
int pingCount = 0, maxPings = 6;
do {
epoch = getLinuxEpoch();
pingCount++;
} while ((epoch == 0) && (pingCount <= maxPings));
if (pingCount > maxPings) {
Serial.println("NTP did not respond");
}
else {
rtc.setEpoch(epoch + GMT_ADJUST);
Serial << "Time value: " << rtc.getEpoch() << '\n';
}
}
Page 264
RTCZero rtc;
WiFiUDP Udp;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) {}
Serial.println("Connecting to WiFi...");
connectToWiFi();
rtc.begin(); // start the clock
getCurrentTime();
showTime();
}
unsigned long getLinuxEpoch()
{
Udp.begin(localPort);
sendNTPPacket(timeServer); // send an NTP packet to NTP server
// wait a bit
delay(1000);
if ( Udp.parsePacket() ) {
Serial.println("NTP time received");
// read data into buffer
Udp.read(packetBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE); // read 48 bytes
unsigned long highWord = word(packetBuffer[40], packetBuffer[41]);
unsigned long lowWord = word(packetBuffer[42], packetBuffer[43]);
// combine the four bytes into a long integer
// should be seconds since Jan 1 1900
unsigned long ntpTime = highWord << 16 | lowWord;
Udp.stop();
// now adjust NTP time to Linux time which starts 70 years later
const unsigned long seventyYears = 2208988800UL;
return (ntpTime - seventyYears);
} else {
Udp.stop();
return 0;
}
}
Page 265
void showTime() {
Serial << rtc.getDay() << '/' << rtc.getMonth() << "/20" <<
rtc.getYear() << " " << rtc.getHours() << ':' << rtc.getMinutes() <<
':' << rtc.getSeconds() << '\n';
}
volatile unsigned long rtcEpoch = 0;
unsigned long lastEpoch = 0;
void setAlarm(){
rtc.setAlarmSeconds(5);
rtc.attachInterrupt(alarmCall);
rtc.enableAlarm(rtc.MATCH_SS); // match the alarm time every minute
}
void alarmCall() {
rtcEpoch = rtc.getEpoch();
}
void loop() {
if(rtcEpoch != lastEpoch) {
lastEpoch = rtcEpoch;
showTime();
}
}
Page 266
#define BUFF_SIZE 81
#include <WiFiNINA.h>
#include "Secret.h"
const char* mySSID = SECRET_SSID;
const char* myPass = SECRET_PASSWORD;
const char pageRequest[] = "GET / HTTP/1.1";
WiFiServer server(80); // port 80
char buffer[BUFF_SIZE];
const long timeOut = 1000;
unsigned long waitStart;
int pageCount = 0;
WiFiClient client;
template<class T> inline Print &operator<<(Print &obj, T arg) {
obj.print(arg); return obj;}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) {}
connectToWiFi();
server.begin(); // start the server
}
Page 267
void connectToWiFi() {
while (WiFi.begin(mySSID, myPass) != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
}
Serial << "WiFi connected\n";
Serial << "Local IP: " << WiFi.localIP() << '\n';
}
void loop() {
client = server.available();
if(client) {
int charCount = clearBuffer();
Serial << "Browser connected\n";
waitStart = millis();
while (client.connected()) {
if(client.available()) {
char c = client.read();
Serial << c;
if(c == '\n' || c == '\r'){
if(strncmp(pageRequest, buffer, 14) == 0) {
sendHTML();
break;
} else {
charCount = clearBuffer();
waitStart = millis();
}
} else {
if(charCount < 79) {
buffer[charCount] = c;
charCount++;
}
}
} else {
// trigger timeout when browser silent
if((unsigned long)millis() - waitStart >= timeOut) {
break;
}
}
}
client.flush();
client.stop();
Serial << "Browser disconnected\n";
}
}
Page 268
int clearBuffer() {
memset(buffer, 0, BUFF_SIZE);
return 0;
}
void sendHTML() {
Serial << "\nSending HTML\n";
// HTTP preamble first
client << "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\n";
client << "Content-Type: text/html\n";
client << "Connection: close\n\n"; // extra linefeed important
// now the HTML forming the web page
client << "<!DOCTYPE HTML>\n";
client << "<html>\n";
client << "Hello from Arduino MKR 1010 Server<br />\n";
pageCount++;
client << "Page served Counter: " << pageCount << '\n';
client << "</html>\n";
}
Page 269
client << "<input type=\"button\" onclick=\"location.href=\'/A\';\" value=\"Click Me\" />\n";
Page 270
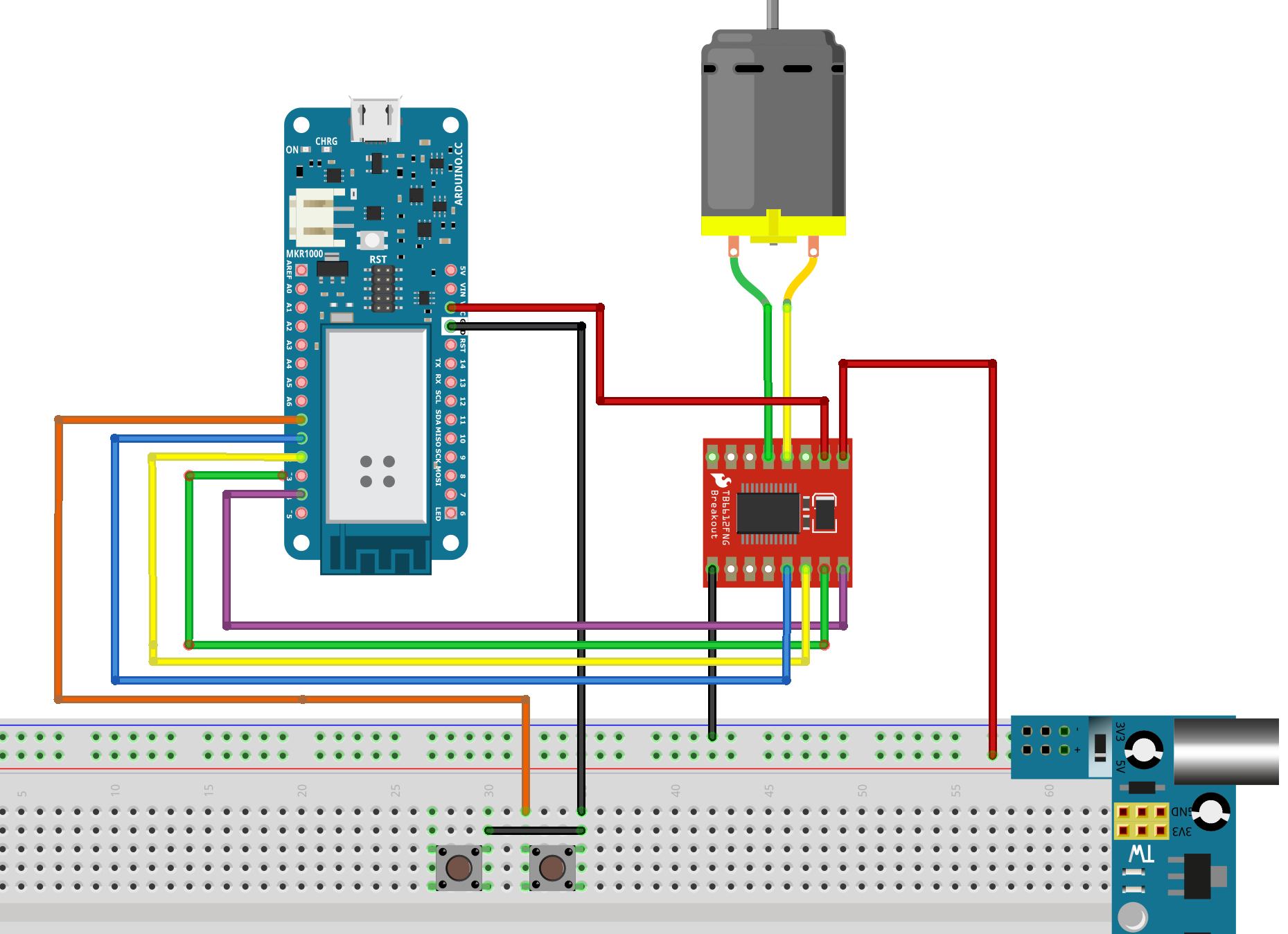
const int PWMA = 4;
const int AIN2 = 3;
const int AIN1 = 2;
const int STBY = 1;
byte motorSpeed = 180;
void setMotorPins() {
pinMode(PWMA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(AIN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(AIN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(STBY, OUTPUT);
}
Page 271
Confession
When coding this program, I committed a cardinal sin. I allowed more than one enum to contain the same literals. At the time, the Arduino compiler was sanguine and everything worked as intended. More recent updates to the toolchain have exposed my error. I am pretty sure my book made it clear on page 26 that you should never do this. I repeatedly defined enum values OPEN and CLOSED. Here for the SwithState enum. This also clashed with a value in a later version of the WiFiNINA library. Please change the enum values to something unique and then use those values in the associated code.
void motorOpen() {
analogWrite(PWMA, motorSpeed);
digitalWrite(AIN1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(AIN2, LOW);
digitalWrite(STBY, HIGH);
}
void motorBrake() {
digitalWrite(AIN1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(AIN2, HIGH);
analogWrite(PWMA, 0);
}
void motorStop() {
digitalWrite(AIN1, LOW);
digitalWrite(AIN2, LOW);
analogWrite(PWMA, 0);
digitalWrite(STBY, LOW);
}
void motorClose() {
analogWrite(PWMA, motorSpeed);
digitalWrite(AIN1, LOW);
digitalWrite(AIN2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(STBY, HIGH);
}
const int LIMIT_CLOSED = 0;
const int LIMIT_OPEN = 16; // Pin A1
enum SwitchStates: int8_t {OPEN, CLOSED}; // switch open or closed
byte closedLimitState = OPEN;
volatile byte newClosedState = OPEN;
byte openLimitState = OPEN;
volatile byte newOpenState = OPEN;
Page 272
void setupLimitSwitches() {
pinMode(LIMIT_CLOSED, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(LIMIT_OPEN, INPUT_PULLUP);
attachInterrupt(LIMIT_CLOSED, setClosedLimit, CHANGE);
attachInterrupt(LIMIT_OPEN, setOpenLimit, CHANGE);
initLimitStates();
}
void setClosedLimit() {
newClosedState = (digitalRead(LIMIT_CLOSED) == LOW) ? CLOSED : OPEN;
}
void setOpenLimit() {
newOpenState = (digitalRead(LIMIT_OPEN) == LOW) ? CLOSED : OPEN;
}
void initLimitStates() {
newClosedState = closedLimitState =
(digitalRead(LIMIT_CLOSED) == LOW) ? CLOSED : OPEN;
newOpenState = openLimitState =
(digitalRead(LIMIT_OPEN) == LOW) ? CLOSED : OPEN;
if(closedLimitState == CLOSED) {
skylightState = FULLY_CLOSED;
} else if(openLimitState == CLOSED) {
skylightState = FULLY_OPEN;
} else {
skylightState = PART_OPEN; // as it can't be moving yet
}
}
Page 273
void checkLimitStates() {
if(newOpenState != openLimitState) {
if(newOpenState == CLOSED) {
motorStop();
skylightState = FULLY_OPEN;
if(Serial) {
Serial << "Stopped in fully open position\n";
}
}
openLimitState = newOpenState;
}
if(newClosedState != closedLimitState) {
if(newClosedState == CLOSED) {
motorStop();
skylightState = FULLY_CLOSED;
if(Serial) {
Serial << "Stopped in fully closed position\n";
}
}
closedLimitState = newClosedState;
}
}
void clearBuffer() {
memset(buffer, 0, BUFF_SIZE);
charCount = 0;
}
void sendHTML() {
client << "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\n";
client << "Content-Type: text/html\n";
if(skylightState == OPENING || skylightState == CLOSING) {
client << "Refresh: 3\n"; // ask for refresh at 3 second intervals
}
client << "Connection: close\n\n"; // extra linefeed important
Page 274
client << "<!DOCTYPE HTML>\n";
client << "<html>\n<head>\n";
client << "<meta name=\"viewport\" content=\"width=device-width, initial-scale=1\">\n";
client << "<title>Skylight Automation</title>\n</head>\n";
client << "<body><div style=\"width:100%; height: 100%; ";
client << "background-color: antiquewhite;\">\n";
client << "<div style=\"text-align: center; border: 3px solid blue;\">\n";
client << "<h1>Automated Skylight</h1><br />\n";
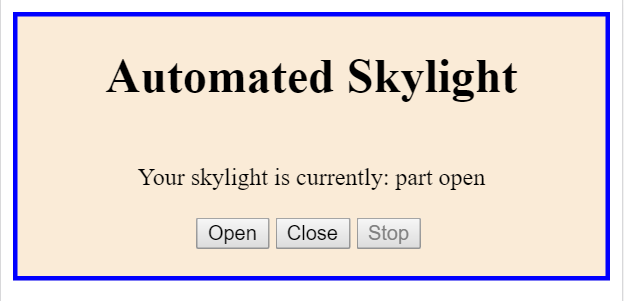
client << "Your skylight is currently: ";
client << stateText[skylightState];
client << "<br /><br />\n";
client << "<input type=\"button\" value=\"Open\" onclick=\"location.href=\'/O';\" ";
if(skylightState != FULLY_CLOSED && skylightState != PART_OPEN) {
client << " disabled ";
}
client << " />\n";
client << "<input type=\"button\" value=\"Close\" onclick=\"location.href=\'/C';\" ";
if(skylightState != FULLY_OPEN && skylightState != PART_OPEN) {
client << " disabled ";
}
client << " />\n";
client << "<input type=\"button\" value=\"Stop\" onclick=\"location.href=\'/S';\" ";
if(skylightState != OPENING && skylightState != CLOSING) {
client << " disabled ";
}
client << " />\n";
client << "<br /><br /></div></div></body></html>\n";
}
Page 275
#define BUFF_SIZE 81
#define BUFF_LIMIT 80
#include <WiFiNINA.h>
#include "Secret.h"
char buffer[BUFF_SIZE];
const long timeOut = 500;
unsigned long waitStart;
int charCount;
enum SkylightStates: int8_t {FULLY_OPEN, FULLY_CLOSED, PART_OPEN,
OPENING, CLOSING};
char stateText[][13] = {"fully open", "fully closed",
"part open", "opening", "closing"};
byte skylightState;
const char* mySSID = SECRET_SSID;
const char* myPass = SECRET_PASSWORD;
const char getRequest[] = "GET /";
WiFiServer server(80); // port 80 is standard
WiFiClient client;
template<class T> inline Print &operator<<(Print &obj, T arg) {
obj.print(arg); return obj;}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) {}
setMotorPins();
setupLimitSwitches();
connectToWiFi();
server.begin(); // start the server
}
void connectToWiFi() {
while (WiFi.begin(mySSID, myPass) != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
}
Serial << "WiFi connected\n";
Serial << "Local IP: " << WiFi.localIP() << '\n';
}
Page 276
void loop() {
if(skylightState == OPENING || skylightState == CLOSING) {
checkLimitStates(); // check for interrupts
}
client = server.available();
if(client) {
waitStart = millis();
clearBuffer();
while (client.connected()) {
if(client.available()) {
char c = client.read();
if(c == '\n' || c == '\r'){
if(strncmp(getRequest, buffer, 5) == 0) {
switch(buffer[5]) {
case ' ': // initial get request
sendHTML();
break;
case 'O': // open button clicked
if(skylightState != OPENING && skylightState != FULLY_OPEN){
skylightState = OPENING;
motorOpen();
}
sendHTML();
break;
case 'C': // close button clicked
if(skylightState != CLOSING && skylightState != FULLY_CLOSED) {
skylightState = CLOSING;
motorClose();
}
sendHTML();
break;
case 'S': // stop button
motorStop();
skylightState = PART_OPEN; // probably
checkLimitStates(); //to make sure
sendHTML();
break;
}
}
break; // escape while loop to close connection
} else {
if(charCount <= BUFF_LIMIT) {
buffer[charCount] = c;
charCount++;
}
}
} else {
if((unsigned long)millis() - waitStart >= timeOut) {break;}
}
if(skylightState == OPENING || skylightState == CLOSING) {
checkLimitStates();
}
}
client.flush();
client.stop();
}
}
Page 277
Page 279
#include <WiFiNINA.h>
#include "Secret.h"
const char* mySSID = SECRET_SSID;
const char* myPass = SECRET_PASSWORD;
template<class T> inline Print &operator<<(Print &obj, T arg) {
obj.print(arg); return obj;}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) {}
connectToWiFi();
connectToResource();
}
#include <WiFiNINA.h>
#include "Secret.h"
const char* mySSID = SECRET_SSID;
const char* myPass = SECRET_PASSWORD;
template<class T> inline Print &operator<<(Print &obj, T arg) {
obj.print(arg); return obj;}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) {}
connectToWiFi();
connectToResource();
}
void connectToResource() {
WiFiClient client;
const char* host = "www.arduino.cc";
const int httpPort = 443;
char* uri = "/reference/en/language/variables/data-types/stringobject/";
if (!client.connectSSL(host, httpPort)) {
Serial << "connection failed\n";
return;
}
client << "GET " << uri << " HTTP/1.1\r\n";
client << "Host: " << host << "\r\n";
client << "Connection: close\r\n\r\n"; // two line terminators
unsigned long timeOut = millis();
while(!client.available()) {
if((unsigned long) millis() - timeOut > 5000) {
Serial << "Client timeout\n";
}
}
while(client.available() ) {
char c = client.read();
Serial << c;
}
Serial << "\nThats All Folks\n";
}
Page 280
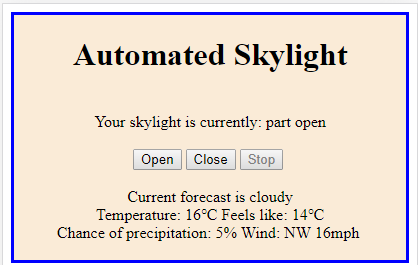
My final program
Please note the service used to lookup weather forecasts for this section of the book is no longer available. The code can still be used as a model for similar services.
If you are interested in my final program and the detail of my chosen service (warts and all) then you can click here for a download.
You would have to sign up for your own API key and (of course) add your own Secret.h.
Fixing MKR 1010 board problems
I discovered some time ago that the MKR WiFi 1010 board can crash and become unresponsive. Something that never happens (in my experience) with board like the Uno or MEGA which are pretty near “bomb proof”. So, I learned how to reset a MKR 1010. If you ever get in a similar jam, just double click the re-set button. You will know that you have got the slightly fiddly double click right when one of the on-board LEDs starts to slowly fade. This is very distinctive. The COM port associated with the board will also have changed temporarily. Once a new program has been uploaded (even Blink) then the COM port will revert and the board will be back in service.
I also managed to do something with my board that meant that the WiFi module became unresponsive. This was resolved by using the “WiFi 101 / WiFiNINA Firmware Updater” option under the “Tools” menu (versions 1 and 2 of the Arduino IDE). The firmware update cleared the problem and restored my board to full functionality.
That triggered a thought. It would be handy to have a program to check that the installed WiFi module firmware was up to date and matched the installed library which will very likely have been updated over time.
#include <SPI.h>
#include <WiFiNINA.h>
template<class T> inline Print &operator<<(Print &obj, T arg) {
obj.print(arg); return obj;}
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {}
Serial << "Firmware Check\n";
if(WiFi.status() == WL_NO_MODULE){
Serial << "Connection to WiFi module failed\n";
Serial << "Status: " << WiFi.status() << '\n';
while(true); // do nothing
}
char fv = *WiFi.firmwareVersion();
char lfv = *WIFI_FIRMWARE_LATEST_VERSION;
if(fv >= lfv){
Serial << "Firmware version " << fv << " up to date\n";
} else {
Serial << "Please update firware to version " << lfv << '\n';
}
}
void loop() {
}
