Practical Arduino C
Chapter 9: Extras
Page 129
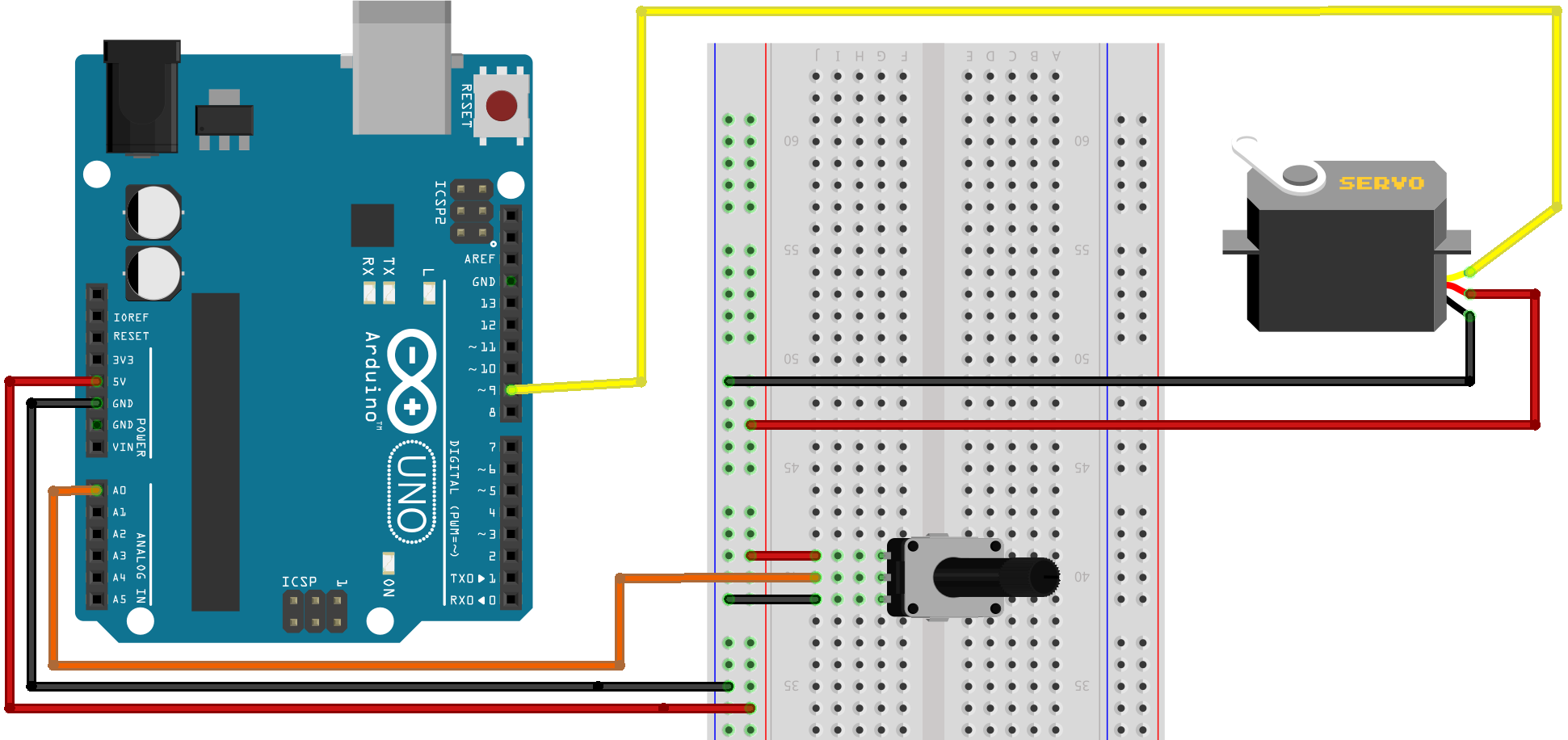
Page 130
#include <Servo.h>
Servo mServo;
const int potPin = 0;
void setup() {
mServo.attach(9);
}
void loop() {
int potVal = analogRead(potPin); // reads the value of the
//potentiometer (0 to 1023)
potVal = map(potVal, 0, 1023, 0, 180); // scale to range 0 to 180
mServo.write(potVal); // sets the servo position
delay(15); // give the servo time to move
//BUT DON’T USE DELAY() FOR REAL
}
Continuous Servo Motors
I wrote a blog post on (the clumsy) building of a small autonomous robot based upon two continuous servo motors.
The robot used an Artificial Neural Network running on an Arduino Nano and an ultrasonic rangefinder to guide it around it's landscape.
The code downloads for my version are available on the projects page.
Page 132
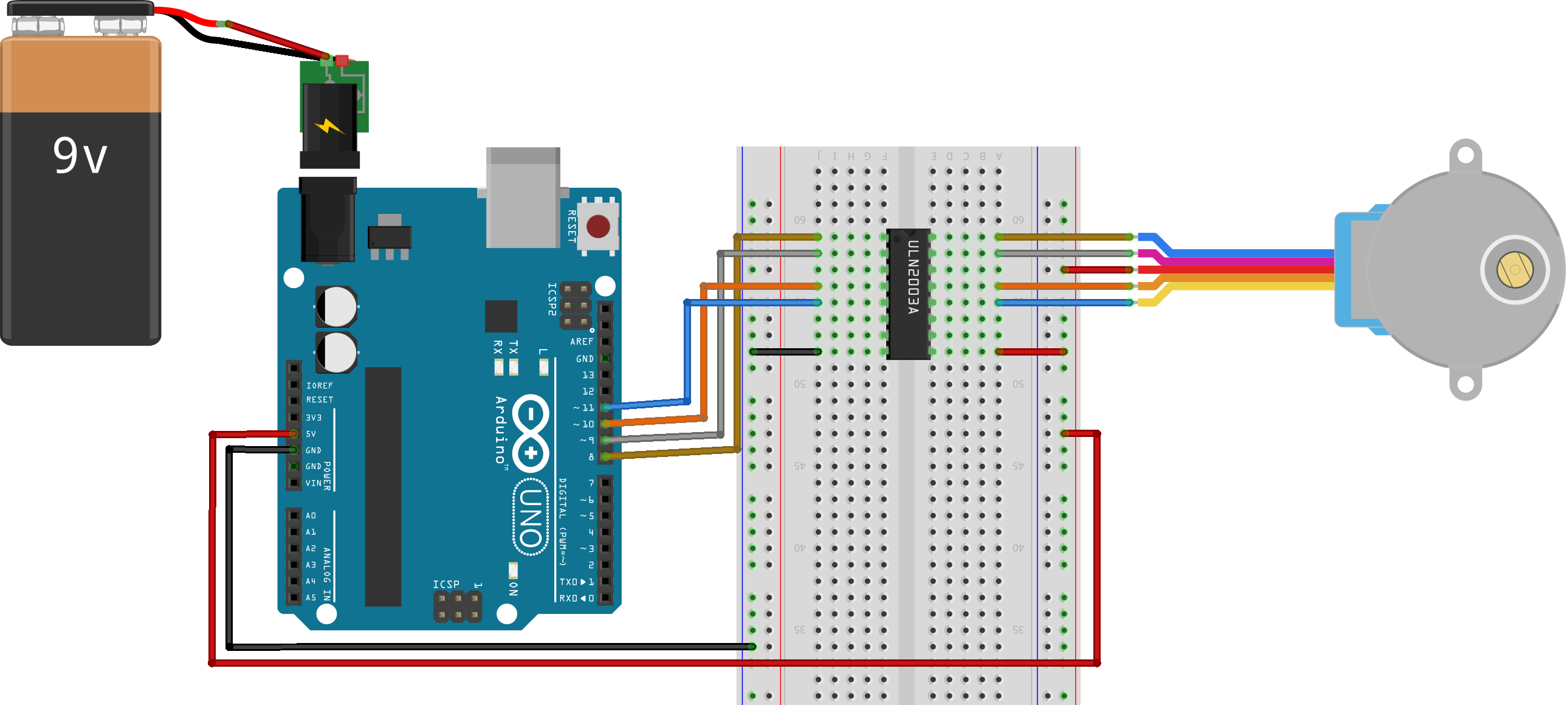
Page 134
#include <Stepper.h>
const int stepsPerRev = 200; // change this for motor step angle
// and any gearbox ratio
Stepper mStepper(stepsPerRev, 8, 9, 10, 11);
void setup() {
mStepper.setSpeed(30); // 30 rpm
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop() {
// step one rev at set speed
Serial.println("Forward");
mStepper.step(stepsPerRev);
delay(500);
// reverse with negative step value
Serial.println("Backwards");
mStepper.step(-stepsPerRev);
delay(500);
}
Page 135
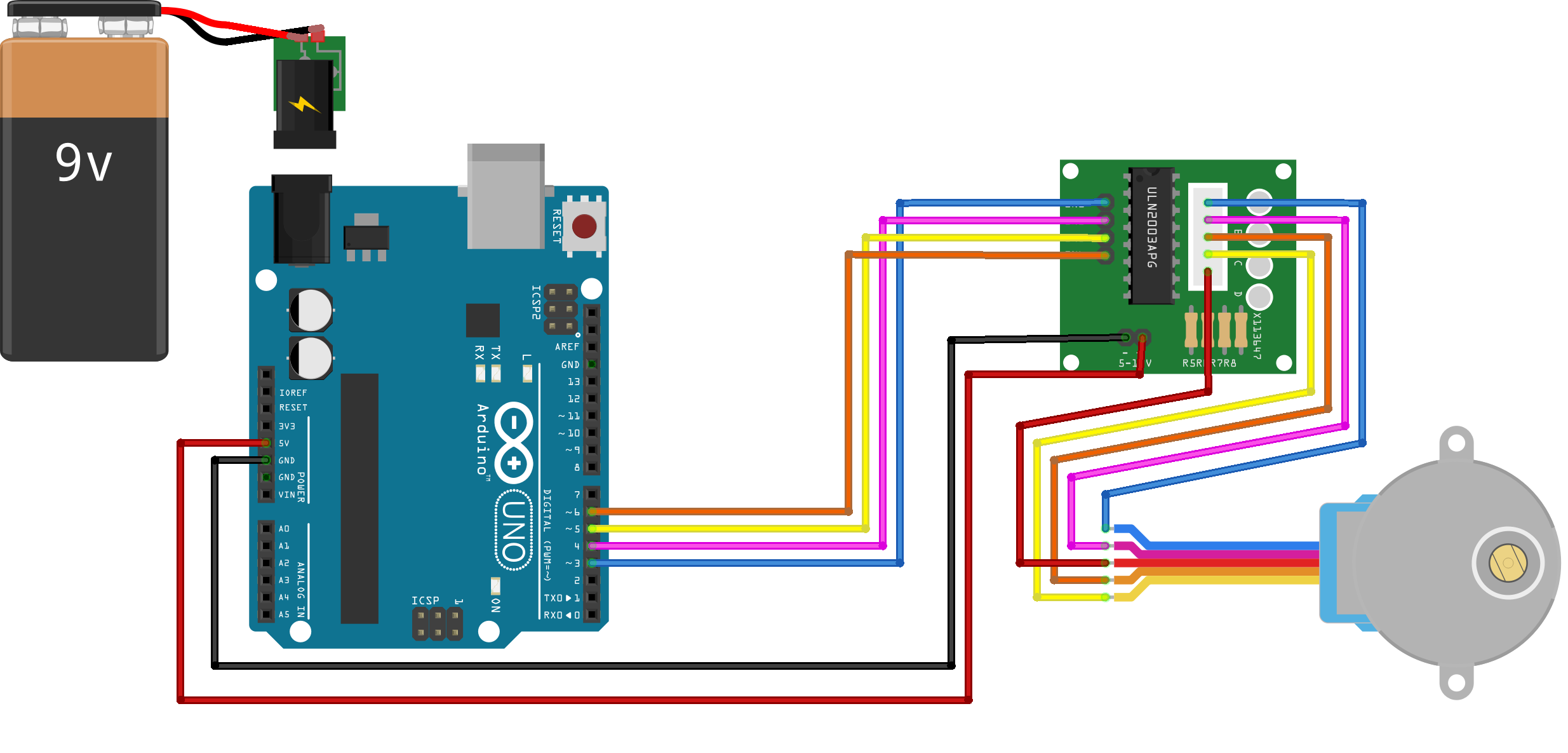
The AccelStepper library can be found at http://www.airspayce.com/mikem/arduino/AccelStepper/index.html
Page 136
const int HALFSTEP = 8;
const int sPin1 = 3; // connect to IN1 on the driver board
const int sPin2 = 4; // IN2
const int sPin3 = 5; // IN3
const int sPin4 = 6; // IN4
AccelStepper stepper(HALFSTEP, sPin1, sPin3, sPin2, sPin4);
void setup() {
stepper.setMaxSpeed(1000.0);
stepper.setAcceleration(100.0);
stepper.setSpeed(200);
stepper.moveTo(8192); // 4 times around
}
void loop() {
if (stepper.distanceToGo() == 0) {
stepper.moveTo(-stepper.currentPosition());
}
stepper.run();
}
